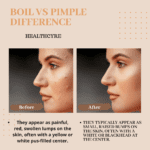
Boil vs. Pimple: Signs, Causes, and Treatments for Each
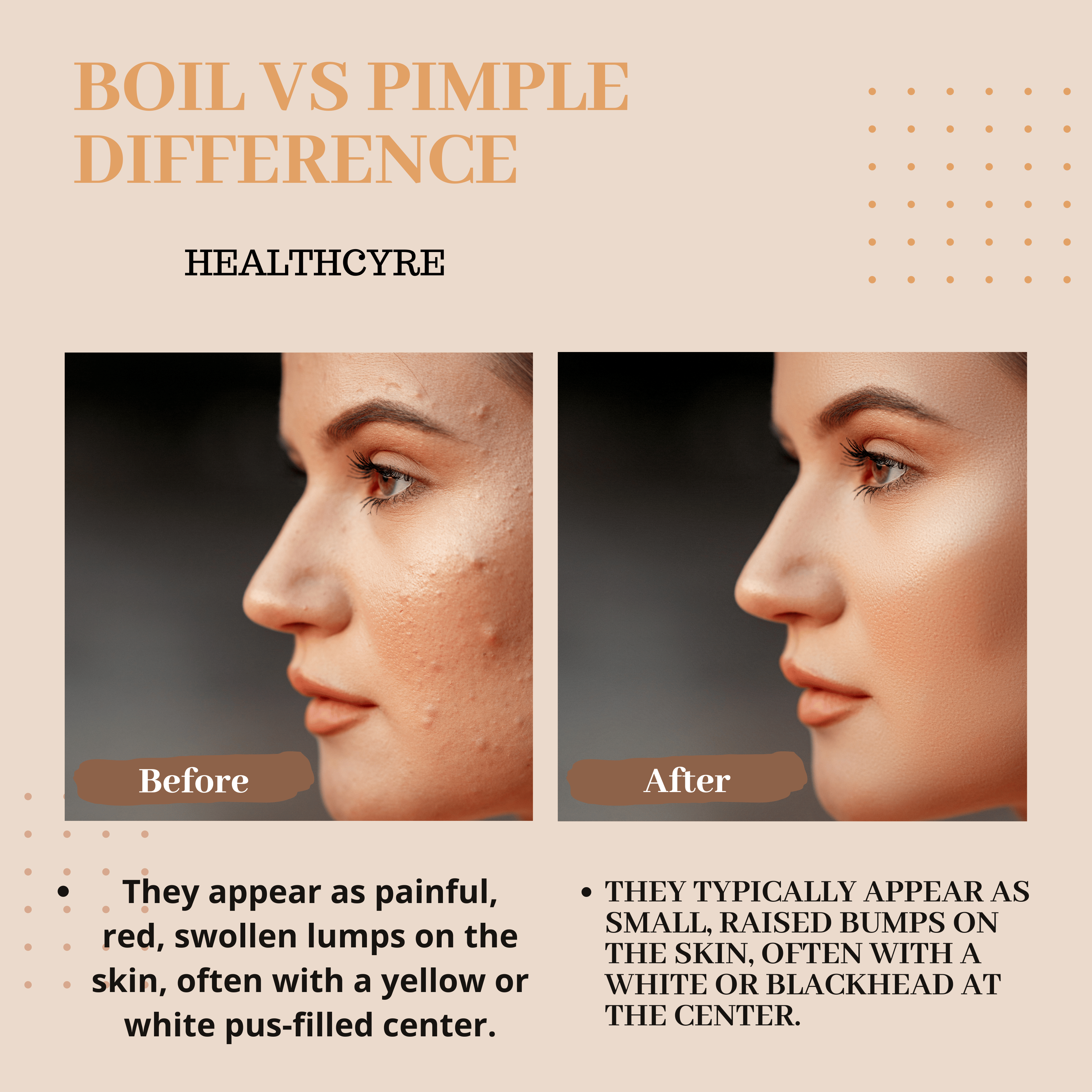
Large pimples and boils can look very similar. They are both swollen, painful lumps filled with a thick, yellowish fluid called pus.
Despite their similarities, pimples and boils are not the same. They may have different bacterial causes and need other treatments to help clear the condition. They also develop on different structures of the skin and in different locations.
This article describes some differences between pimples and boils and how each should be treated.
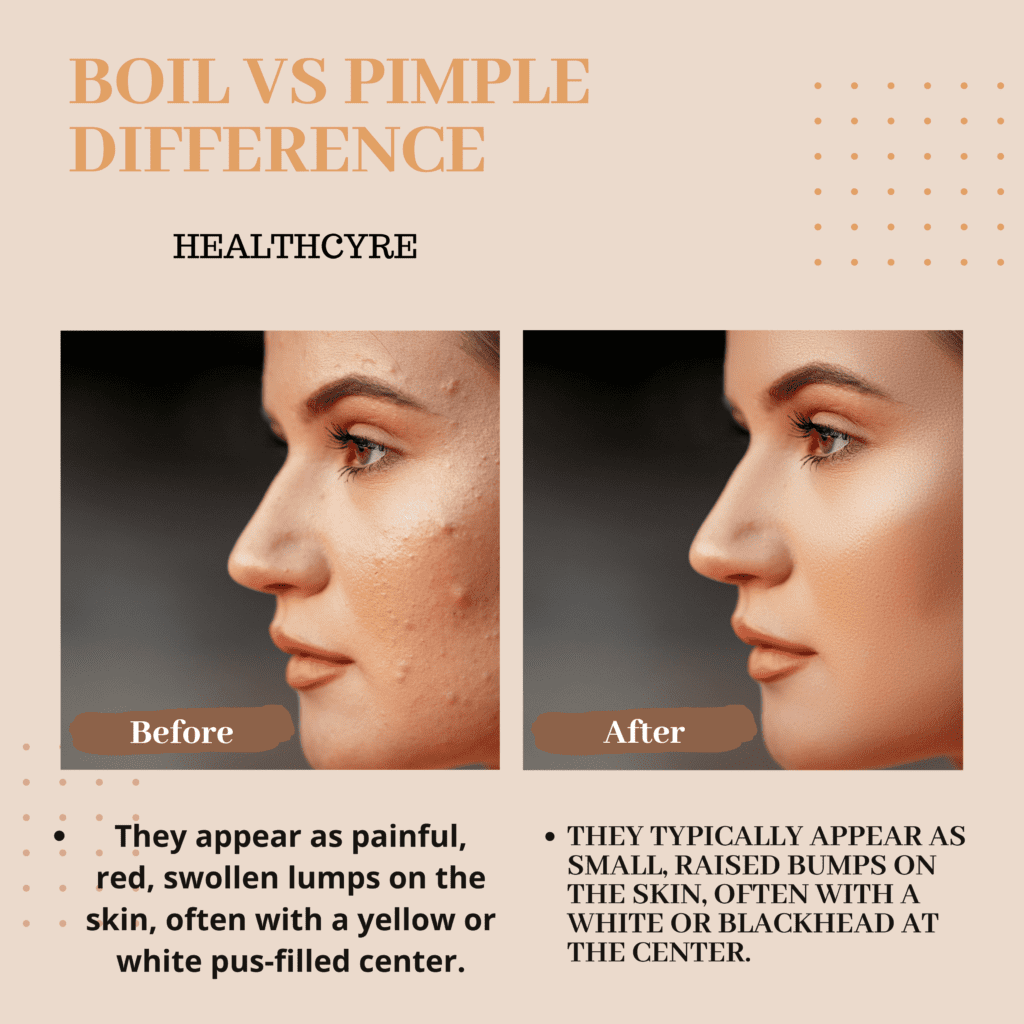
Appearance
Boils and pimples may appear similar at first, but they will change shape and texture with time.
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a damaged growth of hair caused mostly by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. While the bacteria is most usually found on the skin, it can occasionally enter underlying tissues via a skin infraction.1
Acne pimples form when a hair cell gets plugged with dead skin cells and sebum, a kind of skin oil. The obstruction causes bacteria that normally live in the hair to grow rapidly, resulting in a pus-filled pocket known as a pustule. The acne-causing bacteria is a bacteria personally linked to acne
These features account for the variations in appearance between boils and pimples.
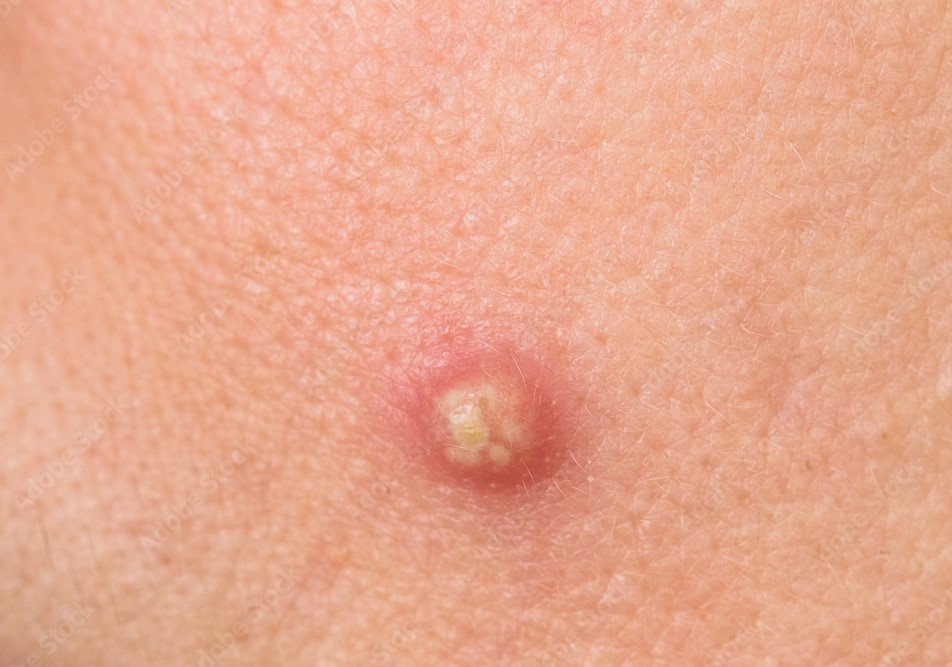
“Boils Unmasked: A Comprehensive Visual Overview”
A boil usually starts as a painful, solid, red lump under the skin’s surface. Over time, generally within a few days, the lump may grow in size, soften, and produce a pus-filled head.
A boil, unlike a pimple, can grow significantly bigger, up to the size of a golf ball. It may start to release pus and clear fluid. In certain circumstances, the infection can extend beyond the hair root to the surrounding tissues, potentially leading to a more serious illness called a condition called cell
Multiple boils may sometimes combine beneath the skin to produce a bigger, pus-filled chamber known as a carbuncle.
“Pimple Unmasked: A Comprehensive Visual Overview”
A pimple tends to be a small pus-filled group that forms within the hair fibers. It can be red, heated to the touch, bloated, and even painful. Unlike boils, which can expand and form a pus-filled head, pimples stay tiny and do not merge into bigger spots.
Chronic acne, a severe form of acne, can resemble boils due to the bigger pimples that may leak pus on their own. Regular pimples, on the other hand, do not exude pus until purposefully or accidentally crushed or “smashed.”
The size of pimples varies, with the most frequent ones ranging from a nail head to a pea. In comparison, acne-like cystic pimples can develop to the size of a coin. It’s important to avoid popping.
Where Are Boils Likely to Be?
Furuncles tend to develop in high-moisture areas of skin where S. aureus is more likely to proliferate and/or where hairy areas of skin rub together and create friction.
Common sites for boils include:
- Groin
- Thighs
- Breasts
- Armpits
Where Are Pimples Likely to Be?
Pimples tend to develop in areas of skin where sebum-producing glands, called sebaceous glands, are densely situated. The most common include:
- Face
- Back
- Upper chest
Treatment
Boils frequently require strong therapy to eliminate the illness and prevent it from developing. Pimples frequently require long-term therapy to manage the underlying processes that cause acne.
How are boils treated?
Boils may usually be treated at home over a few days. This entails emptying the fluid-filled pocket to allow for healing. This can be accomplished by covering the boil with a warm, moist towel several times each day to soften the skin and encourage drainage.1
You should never cut or “pop” a boil because it might drive you into deeper layers of skin and increase the condition.
If a big boil does not respond to home therapy, you should consult a healthcare specialist (such as a dermatologist).
A healthcare physician can recommend medicines if the boil is big, periodic, or located in a sensitive location, such as the ears or nose.1
How Are Pimples Treated?
Pimples can also be treated at home with gentle skin care and over-the-counter (OTC) topical medications like benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid.4
As with boils, you should never “pop” a pimple as doing so can rupture the follicle and force pus into deeper tissues.
Sometimes treatment can go on for months and require ongoing care. If these at-home measures don’t help, you may need to see a dermatologist who can prescribe topical or oral drugs along with specialist procedures.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
Severe furuncles or pimples may not respond to home therapy and require the care of a dermatologist. There are several ways to know when a dermatologist is needed.
Seeking Care for a Boil
You don’t usually need to see a healthcare provider for a small boil. Most will burst and heal on their own.
However, you should seek medical treatment for a boil if:
- It is on your face, nose, or spine.
- It doesn’t heal within two weeks.
- It is large and painful.
- You develop a fever, chills, or other signs of a severe infection.
Seeking Care for a Pimple
Most people will opt to treat pimples at home and only see a healthcare provider when OTC treatments fail.
As a general rule, it is time to see a dermatologist when
- Pimple breakouts are severe, recurrent, or persistent.
- You have a pimple on the armpit, groin, or thigh (as it may turn out to be a boil).
- You get pimples before the age of eight.
- You started taking prescription medications within six months and suddenly had an acne breakout.
- You have developed or are developing acne scars.
- Pimples are causing you distress.
Prevention
While it is not always feasible to avoid the appearance of boils or pimples, you may take some basic actions to lower your risk.
1. To prevent boils, clean any small wounds, scrapes, or scratches right away to prevent germs from infecting the skin.
2. Wash your skin every day with a mild antibacterial soap to keep it clean and clear of bacteria that might cause disease.
3. Wrap any cuts or wounds in a clean bandage while they heal to avoid additional contamination and encourage normal healing.
4. Eat a well-balanced diet and exercise regularly to boost your immune system, which can help avoid infections and lower your chances of developing boils.
Summary
Boils and large pimples look similar but have different causes and treatments. Boils are infected hair follicles; pimples are blocked hair follicles.
Pimples are rarely larger than a dime, and boils can be far larger than that. Pimples are mostly seen on the face, back, and upper chest, while boils are mainly seen in the groin, breast, thigh, and armpit areas.

Box Breathing
The Power of Box…
Tiktok Leggings Legs
TikTok Leggings Legs: A…

How to remove mucus from lungs naturally
If you have extra…

Preventing heart disease?
Unlocking the Heart Health…
Chair Exercises for Lower Back Pain
lower back pain 10…

Acrylic Nails: Beginners
Read the Before Acrylic…
VITAMIN C-NUTRITON SOURCE-
VITAMIN C: BENEFITS When…

Track Marks on Hands
What are track marks?…
Boil vs. Pimple: Signs, Causes, and Treatments for Each
Boil vs. Pimple: Signs,…

How did Kelly Clarkson lose all that weight?
Kill tooth pain nerve…

Kill tooth pain nerve in 3 seconds Permanently
How to kill tooth…

Hair Treatment for Damage hair
1: Introduction I. Importance of…

What Causes White Spots on Skin
When dead cells or…

Ayurvedic Treatment for Depression
Ayurvedic Treatment for Depression…

Brown Rice vs White Rice Nutrition
Studies show that incorporating…

Fat Gain Diet
Unlocking the Power of…

Water Consumption Guidelines
Overview Drinking water is…

What is the Best Excercise to lose Belly fat
The ideal workout to…

Heart Healthy Diet Foods For Beginners
Understanding Heart-Healthy Foods: In…